Synthetics
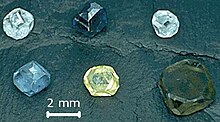 |
| Synthetic diamonds of various colors grown by the high-pressure high-temperature technique |
The majority of commercially available synthetic diamonds are yellow and are produced by so called High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT) processes. The yellow color is caused by nitrogen impurities. Other colors may also be reproduced such as blue, green or pink, which are a result of the addition of boron or from irradiation after synthesis.
 |
| Colorless gem cut from diamond grown by chemical vapor deposition |
At present, the annual production of gem quality synthetic diamonds is only a few thousand carats, whereas the total production of natural diamonds is around 120,000,000 carats (24,000 kg). Despite this fact, a purchaser is more likely to encounter a synthetic when looking for a fancy-colored diamond because nearly all synthetic diamonds are fancy-colored, while only 0.01% of natural diamonds are.
Simulants
 |
| Gem-cut synthetic silicon carbide set in a ring |
Enhancements
Main article: Diamond enhancement
Diamond enhancements are specific treatments performed on natural or synthetic diamonds (usually those already cut and polished into a gem), which are designed to better the gemological characteristics of the stone in one or more ways. These include laser drilling to remove inclusions, application of sealants to fill cracks, treatments to improve a white diamond's color grade, and treatments to give fancy color to a white diamond.Coatings are increasingly used to give a diamond simulant such as cubic zirconia a more "diamond-like" appearance. One such substance is diamond-like carbon—an amorphous carbonaceous material that has some physical properties similar to those of the diamond. Advertising suggests that such a coating would transfer some of these diamond-like properties to the coated stone, hence enhancing the diamond simulant. Techniques such as Raman spectroscopy should easily identify such a treatment.